关于动态连通性
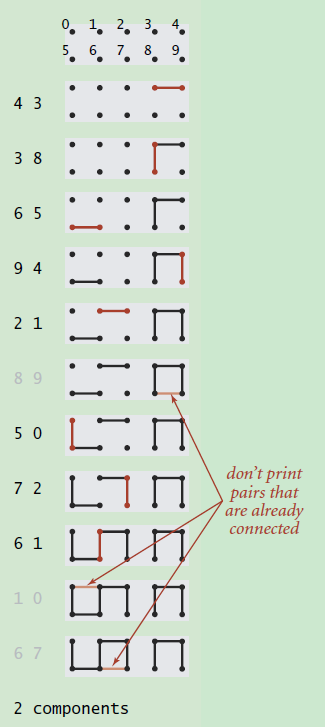
我们看一张图来了解一下什么是动态连通性
假设我们输入了一组整数对,即上图中的(4, 3) (3, 8)等等,每对整数代表这两个points/sites是连通的。那么随着数据的不断输入,整个图的连通性也会发生变化,从上图中可以很清晰的发现这一点。同时,对于已经处于连通状态的points/sites,直接忽略,比如上图中的(8,9)。
动态连通性的应用场景:
网络连接判断: 如果每个pair中的两个整数分别代表一个网络节点,那么该pair就是用来表示这两个节点是需要连通的。那么为所有的pairs建立了动态连通图后,就能够尽可能少的减少布线的需要,因为已经连通的两个节点会被直接忽略掉。
变量名等同性(类似于指针的概念): 在程序中,可以声明多个引用来指向同一对象,这个时候就可以通过为程序中声明的引用和实际对象建立动态连通图来判断哪些引用实际上是指向同一对象。
对问题建模:
在对问题进行建模的时候,我们应该尽量想清楚需要解决的问题是什么。因为模型中选择的数据结构和算法显然会根据问题的不同而不同,就动态连通性这个场景而言,我们需要解决的问题可能是:
给出两个节点,判断它们是否连通,如果连通,不需要给出具体的路径
给出两个节点,判断它们是否连通,如果连通,需要给出具体的路径
就上面两种问题而言,虽然只有是否能够给出具体路径的区别,但是这个区别导致了选择算法的不同,本文主要介绍的是第一种情况,即不需要给出具体路径的Union-Find算法,而第二种情况可以使用基于DFS的算法。
并查集
并查集是若干个不相交的集合,能较快地合并和判断元素所在的集合。
数据结构
并查集的每个元素都是由它和它的父节点(集合内的一个代表)组成,如下表所示:
简单的并查集只需要存储在一个hash表中,key是它本身,value就是它的父节点的值。
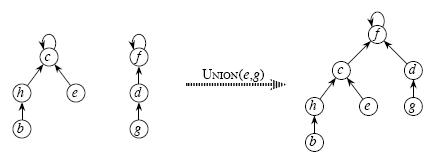
如上图的左边两个集合所示,左边的集合表示为:
初始化
初始化后每一个元素的父亲节点是它本身,即自己是自己的大哥:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 HashMap<Integer,Integer> father; UnionFind(int [] element){ father = new HashMap<>(); Initialization(element); } public void Initialization (int [] nums) for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; ++i) father.put(nums[i],nums[i]); }
查找
查找一个元素所在的集合,其精髓是找到这个元素的终极大boss!这个才是并查集判断和合并的最终依据。 判断两个元素是否属于同一集合,只要看他们是不是最终都归一个终极大boss管, 模板如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public int find (int key) int key_father = key; while (key_father != father.get(key_father)){ key_father = father.get(key_father); } return key_father; }
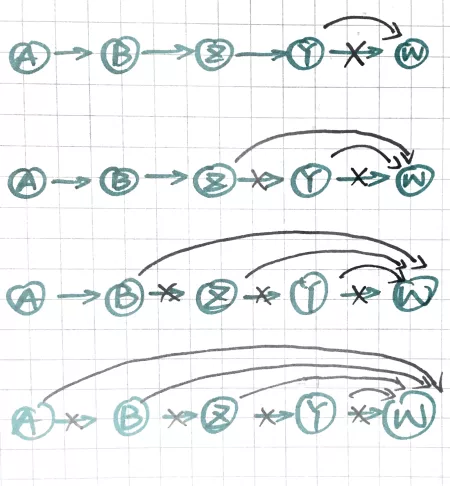
然而,这样的最坏情况下的时间复杂度是\(O(n)\) ,例如这个例子:
a→ b→ x→ y→ w
修正的方法就是在find()之后进行路径压缩:
于是就变为:
代码为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public int find (int key) int key_father = key; while (key_father != father.get(key_father)){ key_father = father.get(key_father); } int temp = key; int temp_father; while (temp != key_father){ temp_father = father.get(temp); father.replace(temp,key_father); temp = temp_father; } return key_father; }
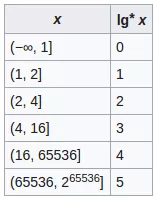
时间复杂度第一次是O(n), 但是多次下来是log*n (见https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iterated_logarithm), 证明略
因为1-5都很小, 所以find基本上是O(1)的操作.
合并
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public void union(int x,int y){ int fa_x = find(x); int fa_y = find(y); if( fa_x != fa_y ){ father.put(fa_x,fa_y); } }
模板
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.HashSet;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.Map;public class UnionFind HashMap<Integer,Integer> father; UnionFind(){ father = new HashMap<>(); } public void add (int key,int fa) if (father.containsKey(key))return ; father.put(key,fa); } public void Initialization (int [] nums) for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; ++i) father.put(nums[i],nums[i]); } public int find (int key) int key_father = key; while (key_father != father.get(key_father)){ key_father = father.get(key_father); } int temp = key; int temp_father; while (temp != key_father){ temp_father = father.get(temp); father.replace(temp,key_father); temp = temp_father; } return key_father; } public void union (int x,int y) int fa_x = find(x); int fa_y = find(y); if ( fa_x != fa_y ){ father.put(fa_x,fa_y); } } public int setNum () Iterator iter = father.entrySet().iterator(); while (iter.hasNext()) { Object key = ((Map.Entry) iter.next()).getKey(); find((Integer) key); } iter = father.entrySet().iterator(); HashSet<Integer> counter = new HashSet<>(); int num = 0 ; while (iter.hasNext()) { Integer val = (Integer)(((Map.Entry) iter.next()).getValue()); if (counter.contains(val)){ continue ; }else { counter.add(val); num+=1 ; } } return num; } }
并查集相关leetcode题
Number of Islands
给定一个二维数组:
其中1为岛屿,0为海洋。如果上下左右相邻,则为同一个岛屿。判断其中有多少个岛屿。
这个题可以用并查集来做。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public int numIslands (char [][] grid) if (grid.length == 0 || grid[0 ].length == 0 )return 0 ; int n = grid.length, m = grid[0 ].length; UnionFind set = new UnionFind(); int index,fa_1,fa_2; for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i+=1 ){ for (int j = 0 ; j < m ; j+=1 ){ if (grid[i][j]=='1' ){ System.out.println(set.father); index = i*m + j; set.add(index,index); if ( i>0 && grid[i-1 ][j]=='1' ){ fa_1 = set.find((index - m)); fa_2 = set.find(index); set.union(fa_1,fa_2); } if (j > 0 && grid[i][j-1 ] == '1' ){ fa_1 = set.find(index - 1 ); fa_2 = set.find(index); set.union(fa_1,fa_2); } } } } return set.setNum();}
这个题是并查集的入门题。但其实并查集更适用于动态变化的集合。这个题有一个更简单的方式,就是dfs:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public void dfs (char grid,int x,int y) if ( x<0 || y<0 || x>= grid.length || y >= grid[0 ].length || grid[x][y]=='0' ){ return ; } if (grid[x][y]=='1' ){ grid[x][y]='0' ; dfs(grid,x+1 ,y); dfs(grid,x,y+1 ); dfs(grid,x-1 ,y); dfs(grid,x,y-1 ); } } public int numIslands (char [][] grid) int i,j; int nums = 0 ; for (i = 0 ; i < grid.length ; i+=1 ){ for (j = 0 ; j < grid[i].length ; j+=1 ){ if (grid[i][j]=='1' ) { dfs(grid, i, j); nums += 1 ; } } } return nums; }
Number of Islands II
这道题是上道题的升级版——动态变化的连通图。很明显用并查集是最好的。
需要注意的是,不像上一题,遍历时只需要遍历左下。这一题的岛屿状态是动态的,因此必须同时遍历上下左右四个方向才行。
此处是这道题的解答:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 class Solution public List<Integer> numIslands2 (int m, int n, int [][] positions) if (positions == null || positions.length == 0 || m == 0 || n == 0 ) { return new ArrayList<Integer>(); } int [] island = new int [m * n + 1 ]; ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>(); int current = 0 ; for (int [] position : positions) { int x = position[0 ]; int y = position[1 ]; int index = x * n + y + 1 ; current++; island[index] = index; if (x != m - 1 && island[index + n] != 0 && union(index, index + n, island)) { current--; } if (x != 0 && island[index - n] != 0 && union(index, index - n, island)) { current--; } if (y != n - 1 && island[index + 1 ] != 0 && union(index, index + 1 , island)) { current--; } if (y != 0 && island[index - 1 ] != 0 && union(index, index - 1 , island)) { current--; } result.add(current); } return result; } private boolean union (int a, int b, int [] array) int fa_a = find(a, array); int fa_b = find(b, array); if (fa_a == fa_b) { return false ; } array[fa_a] = fa_b; return true ; } private int find (int i, int [] array) int fa = array[i]; while (array[fa] != fa) { fa = array[fa]; } int next = array[i]; while (next != fa) { array[i] = fa; i = next; next = array[next]; } return fa; } }
Graph Valid Tree
给一个无向连通图,判断是不是一棵树。
1 2 输入:n = 5` 和边集 edges = [[0, 1], [0, 2], [0, 3], [1, 4]] 输出:true
用连通图,每遍历到一条边前,先判断两点是不是属于一个集合。如果属于同一个集合,那就会变成环形,就不能是树了。
需要注意的是,如果最后整个网络变成了森林,也不行。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public boolean validTree (int n, int [][] edges) if ( n == 0 )return true ; int i; UnionFind set = new UnionFind(); for (i=0 ;i<n;i+=1 ){ set.add(i); } for (int [] e : edges){ if ( set.find(e[0 ]) == set.find(e[1 ]) ){ return false ; }else { set.union(e[0 ],e[1 ]); } } if (set.setNums==1 ){ return true ; }else { return false ; } }
Number of Connected Components in an Undirected Graph
给一个无向连通图,判断有几个联通块。
1 2 输入:n = 5` 和边集 edges = [[0, 1], [1, 2], [2, 3], [3, 4]] 输出:1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public int countComponents (int n, int [][] edges) if ( n == 0 )return 0 ; if ( edges.length ==0 )return n; int i; UnionFind set = new UnionFind(); for (i=0 ;i<n;i+=1 ){ set.add(i); } for (int [] e : edges){ set.union(e[0 ],e[1 ]); } return set.setNums; }
Friend Circles
有n个人,给出一个矩阵M表示n个人互相的关系。求这n个人一共有多少个朋友圈。
1 2 3 4 5 输入: [[1,1,0], [1,1,0], [0,0,1]] 输出: 2
这道题直接用联通图做就好了。输出集合的个数即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public int findCircleNum (int [][] M) if ( M.length == 0 || M[0 ].length == 0 )return 0 ; int n = M.length; int i,j; UnionFind set = new UnionFind(); for ( i = 0 ; i < n ; i += 1 ){ set.add(i); } for ( i = 0 ; i < n ; i+=1 ){ for ( j = i + 1 ; j < n ; j += 1 ){ if ( M[i][j] == 1 ){ set.union(i,j); } } } return set.setNums; }
其实这道题与 200.Number of Islands 是一样的,也可以用dfs来做。此处省略。
Surrounded Regions
给一个矩阵,里面元素是X或O。如果一个O的连通块被X完全围住,就将O全部改成X。例如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 输入: X X X X X O O X X X O X X O X X 输出: X X X X X X X X X X X X X O X X
这道题也可以用并查集来做。我们只需要稍微改一下并查集,在并或查的时候加入一个boolean 的flag,来表示这个连通块是否在于边界处相连即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 class Solution class UnionFind HashMap<Integer,Integer> father; HashMap<Integer,Boolean> hash; int setNums; UnionFind(){ father = new HashMap<>(); hash = new HashMap<>(); setNums = 0 ; } public void add (int key,boolean hash) if (father.containsKey(key))return ; father.put(key,key); this .hash.put(key,hash); setNums+=1 ; } public void Initialization (int [] nums) for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; ++i) father.put(nums[i],nums[i]); } public int find (int key) int key_father = key; while (key_father != father.get(key_father)){ key_father = father.get(key_father); } int temp = key; int temp_father; while (temp != key_father){ temp_father = father.get(temp); if (hash.get(temp)){ hash.replace(temp_father,true ); } if (hash.get(temp_father)){ hash.replace(temp,true ); } father.replace(temp,key_father); temp = temp_father; } return key_father; } public void union (int x,int y) int fa_x = find(x); int fa_y = find(y); if ( fa_x != fa_y ){ if (hash.get(fa_x)){ hash.replace(fa_y,true ); } if (hash.get(fa_y)){ hash.replace(fa_x,true ); } father.put(fa_x,fa_y); setNums-=1 ; } } } public void solve (char [][] board) if (board.length ==0 || board[0 ].length == 0 )return ; int i,j,index; int n = board.length ; int m = board[0 ].length ; UnionFind set = new UnionFind(); for ( i = 0 ; i < n ; i+=1 ){ for ( j = 0 ; j < m ; j += 1 ){ if ( board[i][j] == 'O' ){ index = i * m + j; if ( i == 0 || i == n - 1 || j == 0 || j == m - 1 ){ set.add(index,true ); }else { set.add(index,false ); } if ( i > 0 && board[i-1 ][j] == 'O' ){ set.union(index,index - m); } if (j > 0 && board[i][j-1 ] == 'O' ){ set.union(index,index-1 ); } } } } for ( i = 0 ; i < n ; i+=1 ){ for ( j = 0 ; j < m ; j += 1 ){ if ( board[i][j] == 'O' ){ index = i * m + j; if (!set.hash.get(set.find(index))){ board[i][j] = 'X' ; } } } } } }
但因为这道题不是一个“动态连通”图。并不适用于并查集。其实用DFS就已经很好做了。首先遍历边界,如果边界上有O,就进行DFS,然后把这些与外界接触的O连通图的flag弄为true。这样所有被围起来的O就是fause。到最后统一置为X即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 public void dfs (char [][] board, boolean [] hash, int i , int j, int n,int m) int [][] dir = {{-1 ,0 },{1 ,0 },{0 ,1 },{0 ,-1 }}; int i1,j1; for (int [] d : dir){ i1 = i + d[0 ]; j1 = j + d[1 ]; if ( i1< 0 || i1 >= n || j1 < 0 || j1 >= m ){ continue ; } if ( !hash[i1 * m + j1] && board[i1][j1] == 'O' ){ hash[i1 * m + j1] = true ; dfs(board,hash,i1,j1,n,m); } } } public void solve (char [][] board) if ( board.length == 0 || board[0 ].length == 0 )return ; int i,j; int n = board.length; int m = board[0 ].length; boolean [] hash = new boolean [n*m]; for (i = 0 ; i < n ; i +=1 ){ if (!hash[i * m ] &&board[i][0 ] == 'O' ){ hash[i * m ] = true ; dfs(board,hash,i,0 ,n,m); } if (!hash[i * m + m - 1 ] &&board[i][m-1 ] == 'O' ){ hash[i * m + m - 1 ] = true ; dfs(board,hash,i,m-1 ,n,m); } } for (j = 0 ; j < m ; j +=1 ){ if (!hash[j] &&board[0 ][j] == 'O' ){ hash[j] = true ; dfs(board,hash,0 ,j,n,m); } if (!hash[(n-1 )*m + j] &&board[n-1 ][j] == 'O' ){ hash[(n-1 )*m + j] = true ; dfs(board,hash,n-1 ,j,n,m); } } for (i = 0 ; i < n ; i+=1 ){ for ( j = 0 ; j < m ; j+=1 ){ if (board[i][j] == 'O' && !hash[ i*m + j ]){ board[i][j] = 'X' ; } } } }
Redundant Connection
这道题给了一个无向连通图。要从中取出一条边,使得它成为一棵树。如果有多个解,输出input中最后一个出现的边。
Example 1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Input: [[1,2], [1,3], [2,3]] Output: [2,3] Explanation: The given undirected graph will be like this: 1 / \ 2 - 3
Example 2:
1 2 3 4 5 6 Input: [[1,2], [2,3], [3,4], [1,4], [1,5]] Output: [1,4] Explanation: The given undirected graph will be like this: 5 - 1 - 2 | | 4 - 3
思路:这道题还是直接用并查集就可以。需要记录哪条边的加入使得树出现了环,即判断哪两个点在加入这条边之前就属于同一个集合。
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public int [] findRedundantConnection(int [][] edges) { int j,i=0 ; int result_i = -1 ; boolean flag; UnionFind set = new UnionFind(); for (int [] e : edges){ flag = false ; for ( j = 0 ; j < 2 ; j += 1 ){ if (!set.father.containsKey(e[j])){ flag = true ; set.add(e[j]); } } if (!flag && (set.find(e[0 ]) == set.find(e[1 ]))){ result_i = i; } set.union(e[0 ],e[1 ]); i+=1 ; } if (result_i==-1 ){ return new int [2 ]; } return edges[result_i]; }
Longest Consecutive Sequence
这道题给了一个数组int[] nums = {100,4,200,1,3,2},要输出连续数字的最大个数4。
当然了可以用并查集来做,需要改动一下并查集,让它支持对每个set里的元素个数计数。最后输出最多元素的set的元素个数即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 class Solution class UnionFind HashMap<Integer,Integer> father; HashMap<Integer,Integer> eleNums; int setNums; UnionFind(){ father = new HashMap<>(); eleNums = new HashMap<>(); setNums = 0 ; } public void add (int key) if (father.containsKey(key))return ; father.put(key,key); eleNums.put(key,1 ); setNums+=1 ; } public void Initialization (int [] nums) for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; ++i) father.put(nums[i],nums[i]); } public int find (int key) int key_father = key; while (key_father != father.get(key_father)){ key_father = father.get(key_father); } int temp = key; int temp_father; while (temp != key_father){ temp_father = father.get(temp); eleNums.replace(key_father,eleNums.get(key_father)+eleNums.get(temp)); eleNums.replace(temp,0 ); father.replace(temp,key_father); temp = temp_father; } return key_father; } public void union (int x,int y) int fa_x = find(x); int fa_y = find(y); if ( fa_x != fa_y ){ father.put(fa_x,fa_y); eleNums.replace(fa_y,eleNums.get(fa_y)+eleNums.get(fa_x)); eleNums.replace(fa_x,0 ); setNums-=1 ; } } } public int longestConsecutive (int [] nums) if (nums.length==0 )return 0 ; int ans = 0 ; UnionFind set = new UnionFind(); for (int e : nums){ set.add(e); if (set.father.containsKey(e-1 )){ set.union(e,e-1 ); } if (set.father.containsKey(e+1 )){ set.union(e,e+1 ); } } for (int e:nums){ if (ans < set.eleNums.get(e)){ ans = set.eleNums.get(e); } } return ans; } }
但其实我一开始就被并查集给限制死了。这道题其实有更快的做法,就是先对数组排序!代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public int longestConsecutive (int [] nums) if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 ) return 0 ; Arrays.sort(nums); int longest = 1 ; int l = 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (nums[i] - nums[i - 1 ] == 1 ) { l++; } else if (nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ]) { continue ; } else { longest = Math.max(l, longest); l = 1 ; } } longest = Math.max(l,longest); return longest; }
Accounts Merge
给了一个accouts的list。list当中的每个元素accounts[i]是一个string list:accounts[i][0]代表名字,剩下的就是这个人的邮箱。
我们的目标是合并这些list:
输出每个人的账号列表accounts[j]
如果两个人名相同,但账号不同,这可能是人重名了
一个人最初可以拥有任意数量的账号,但所有这些账号都归属于同一个人
输出:
[人名,账号列表],账号列表要排序
样例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Input: accounts = [ ["John", "johnsmith@mail.com", "john00@mail.com"], ["John", "johnnybravo@mail.com"], ["John", "johnsmith@mail.com", "john_newyork@mail.com"], ["Mary", "mary@mail.com"]] Output: [ ["John", 'john00@mail.com', 'john_newyork@mail.com', 'johnsmith@mail.com'], ["John", "johnnybravo@mail.com"], ["Mary", "mary@mail.com"]]
我们可以看到,第1、5行的John一定是同一个人;但不一定与第4行的人是同一人,因此这两个人不能合并
参考资料
九章算法高级班笔记2.数据结构(上) 并查集(Union-Find)算法介绍