大纲
线性
队列 - Queue
栈 - Stack
哈希 - Hash
树形
堆/优先队列 - Heap / Priority Queue
Tire
TreeMap
Queue
复杂度
\(O(1)\) Push
\(O(1)\) Pop
\(O(1)\) Top
一般用在BFS
Stack
\(O(1)\) Push
\(O(1)\) Pop
\(O(1)\) Top
栈
例题1,Min Stack
实现一种支持求min()的栈
例如给7,9,10,2,1
依次加入栈时,会有当前的最小值。即:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |-----| 1 -> min = 1 |-----| 2 -> min = 2 |-----| 10 -> min = 7 |-----| 9 -> min = 7 |-----| 7 -> min = 7 |-----|
分析:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 加入一开始将7push进去: |-----| 7 -> min = 7 |-----| 然后我们加入9,将9与min比较,得到新的min = 7 |-----| 9 -> min = 7 |-----| 7 -> min = 7 |-----| 再加入10,将10与min比较,得到新的min = 7 |-----| 10 -> min = 7 |-----| 9 -> min = 7 |-----| 7 -> min = 7 |-----| 再加入2,将2与min比较,得到新的min = 2 |-----| 2 -> min = 2 |-----| 10 -> min = 7 |-----| 9 -> min = 7 |-----| 7 -> min = 7 |-----| 再加入1,将1与min比较,得到新的min = 1 |-----| 1 -> min = 1 |-----| 2 -> min = 2 |-----| 10 -> min = 7 |-----| 9 -> min = 7 |-----| 7 -> min = 7 |-----|
那么我们可以把右边的最小值放在一个栈里,我们称它为”最小栈“——表示当前栈元素里的最小值。相当于
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 原栈 最小栈 |-----| |-----| 1 1 |-----| |-----| 2 2 |-----| |-----| 10 7 |-----| |-----| 9 7 |-----| |-----| 7 7 |-----| |-----|
当我们想pop时,只需要同时把最小栈的栈顶也pop出去就好了!!!!!
例题2, Implement Queue with Stack
我们先研究一下队列和栈,假如我们依次将7,9,10,2,1放入队列和栈,就会变成这样:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 队列 栈 |-----| |-----| 1 <-- tail 1 <-- tail |-----| |-----| 2 2 |-----| |-----| 10 10 |-----| |-----| 9 9 |-----| |-----| 7 <-- head 7 <-- head |-----| |-----|
将上面的队列依次pop出来,那么就会得到7,9,10,2,1
将上面的栈依次pop出来,就会得到1,2,10,9,7
也就是说,此时数据是相反的。那如果我们再用一个栈,那就会把数据再反过来一次。
队列和栈都是顺序插入的,区别在于队列的出口方向和栈的出口方向是相反的,利用这个性质,如果我们将元素按照顺序插入栈后,再一个个弹出并反向插入另一个栈,那么这第二个栈的出口顺序就和队列是一样的了。所以我们构造两个栈,所有新加的元素都加入输入栈,一旦要出队列时,我们便将输入栈的元素都反向加入输出栈,再输出。需要注意的是,如果输出栈不为空时,说明当前要输出的元素还在输出栈中,所以我们就暂时不用将输入栈的元素加入输出栈(而且加入后也会导致顺序错误)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 Stack<Integer> input; Stack<Integer> ouput; /** Initialize your data structure here. */ public MyQueue() { input = new Stack<>(); ouput = new Stack<>(); } /** Push element x to the back of queue. */ public void push(int x) { input.push(x); } /** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */ public int pop() { if(ouput.empty()){ // 将input中的所有元素全部放入output while (!input.empty()){ouput.push(input.pop());} } // 输出最后放入的元素 return ouput.pop(); } /** Get the front element. */ public int peek() { if(ouput.empty()){ // 将input中的所有元素全部放入output while (!input.empty()){ouput.push(input.pop());} } // 输出最后放入的元素 return ouput.peek(); } /** Returns whether the queue is empty. */ public boolean empty() { return input.empty() && ouput.empty(); }
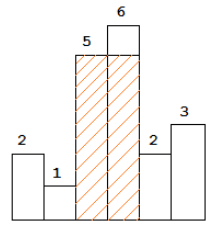
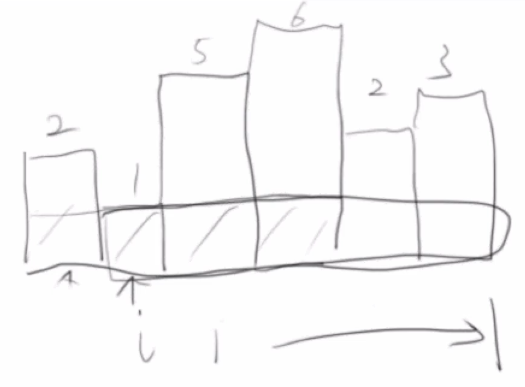
例题3,Largest Rectange in Histogram
在一个直方图上找到一个最大的矩形。如下图所示:
暴力思路
枚举所有可能的矩形
1 2 3 for i 起点 for j 终点 area = (j - i) * minH(i,j)
暴力方案:\(O(n^3)\)
优化一下:minH(i,j) 可以在遍历j的过程中记录下来,那么复杂度就变成了\(O(n^2)\)
在此优化
我们看一下这个情况:
j从i开始到结尾,由于i的高度为1,导致了j怎么扫,最高高度只能为1
如果i向左边延伸一格,那么就会比上面那个大
可以发现我们扫了很多无用状态
换一种思路,先对高度循环:
假设当前高度为2,那么向右边扫,最多只能到第一个比2小的地方。 --> 21
假设当前高度为1,那么可以向左向右扫到第一个比1小(不存在),因此1可以扫n格 --> 1*6
假设当前高度为5,可以向左扫到自己,向右可以扫到6 ---> 5 * 2
.....
总结:对于每个高度来说,只能向左或者向右扫到第一个比它小的元素!
这样的复杂度是\(O(n^2)\)
再次优化
用栈优化寻找一边较小的元素
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 2 1 5 6 2 3 1. 最开始 栈为空2. 对于2 来说,那就先把2 入栈 [2 ] 3. 对于1 来说,1 比2 小,那么2 右边第一个比它小的元素就是1. 那么2 的状态确定了,那就把2 弹出来,而2 的最高面积 = 2 *(1 - 0 ) = 2 [1 ] 4. 对于5 来说,状态暂时未知,先入栈 [1 ,5 ] 5. 对于6 来说,状态暂时未知,入栈 [1 ,5 ,6 ] 6. 对于2 来说,2 比6 小,那么6 右边第一个比它小的一定是2. 那么6 的最大面积 = 6 *(4 -2 -1 ) = 6 (4 是2 的idx,2 是5 的idx) 7. 继续向前看,看5. 那么就可以确定5 的最大面积 = 5 *(4 -1 -1 ) = 10 8. 此时2 大于栈顶了,因此先把2 入栈 [1 ,2 ] ... 到最后再设置一个高度为0 ,然后依次把里面的元素pop出来
复杂度:\(O(n)\)
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 private int getHeights (int idx, int [] heights) if (idx >= heights.length || idx < 0 ) return 0 ; else return heights[idx]; } public int largestRectangleArea (int [] heights) if (heights.length == 0 ) return 0 ; if (heights.length == 1 ) return heights[0 ]; Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); stack.push(-1 ); int max = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i <= heights.length; ){ if (getHeights(i, heights) >= getHeights(stack.peek(), heights)){ stack.push(i); ++i; continue ; } while (!stack.empty() && getHeights(i, heights) < getHeights(stack.peek(), heights)) { int lastIdx = stack.pop(); max = Math.max(max, (i - stack.peek() - 1 ) * getHeights(lastIdx, heights)); } } return max; }
例题4,Max Tree
给一个数组[2,5,6,0,3,1] 。要将这个数组建成一个二叉树。根节点是最大的元素,左子树是将左边的数字传进去,最大值作为根节点
直观思路
递归方法,建树。复杂度很高\(O(n^2)\)
优化方法
跟上面一样
单侧较大值问题
Next Greater Element I
给一个数组nums1和nums2.其中nums1是nums2的子集。令nums1[i] 在nums2的位置是idx.求 在nums2的[idx...n] 之间比nums2[idx]较大的值是多少。
思路:栈维护当前未解决的数字
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public int [] nextGreaterElement(int [] nums1, int [] nums2) { int [] result = new int [nums1.length]; Arrays.fill(result, -1 ); HashMap<Integer, Integer> key2Idx = new HashMap<>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums1.length; ++i){ key2Idx.put(nums1[i], i); } Stack<Integer> idxStack = new Stack<>(); idxStack.push(0 ); for (int i = 1 ; i < nums2.length; ++i){ while (!idxStack.empty() && nums2[i] > nums2[idxStack.peek()]){ int minerIdx = idxStack.pop(); if (key2Idx.containsKey(nums2[minerIdx])){ result[key2Idx.get(nums2[minerIdx])] = nums2[i]; } } idxStack.push(i); } return result; }
Next Greater Element II
给一个数组,求元素nums[i] 的从[i]到[i+nums.length] 的第一个较大的值。
思路:由于涉及到回旋的问题,因此要多循环一圈
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public int [] nextGreaterElements(int [] nums) { if (nums.length == 0 ) return nums; int [] result = new int [nums.length]; Arrays.fill(result, -1 ); Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < 2 *nums.length; ++i){ while (!stack.empty() && nums[i%nums.length] > nums[stack.peek()]){ result[stack.pop()] = nums[i%nums.length]; } stack.push(i%nums.length); } return result; }
骚操作:利用数组替代栈
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public int [] nextGreaterElements(int [] nums) { int [] stack = new int [2 * nums.length]; int top = -1 ; int [] res = new int [nums.length]; Arrays.fill(res, -1 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length * 2 ; i++) { int idx = i % nums.length; while (top >= 0 && nums[stack[top]] < nums[idx]) res[stack[top--]] = nums[idx]; stack[++top] = idx; } return res; }
Daily Temperatures
给一个数组,代表每天的温度。求每天:要等多少天才可以等到温度更高。
一样的思路
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public int [] dailyTemperatures(int [] temperatures) { int [] result = new int [temperatures.length]; if (temperatures.length <= 1 ) return result; Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < result.length; ++i){ while (!stack.empty() && temperatures[i] > temperatures[stack.peek()]){ result[stack.peek()] = i - stack.pop(); } stack.push(i); } return result; }
132 Pattern
给一个数组,寻找类似132这种顺序的序列,也就是中间最大,右边较小,左边最小
一开始我的思路是:从左往右遍历,记录当前最小值;如果当前值比最小值大,就再去右边搜索是否存在比最小值大一点,且比这个值小一点的数字。这样复杂度是\(O(n^2)\)
好一点的操作我没有想到:从后往前扫;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public boolean find132pattern (int [] nums) Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); int last = Integer.MIN_VALUE; for (int i = nums.length - 1 ; i >= 0 ; --i){ while (!stack.isEmpty() && nums[i] > stack.peek()){ last = stack.pop(); } stack.push(nums[i]); if (nums[i] < last) return true ; } return false ; }
括号匹配问题
Valid Parentheses
给一个字符串,其中元素为{},(),[]。判断括号是否合法
思路:用栈!!!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 private boolean isMatch (char a, char b) return (a == '{' && b == '}' ) || (a == '[' && b == ']' ) || (a == '(' && b == ')' ); } public boolean isValid (String s) if (s.length() <= 1 )return false ; Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); ++i){ if (s.charAt(i) == '[' || s.charAt(i) == '{' || s.charAt(i) == '(' ){ stack.push(s.charAt(i)); } else { if (stack.empty() || !isMatch(stack.pop(),s.charAt(i))) return false ; } } return true ; }
Longest Valid Parentheses
给一个字符串,其中元素为() 。判断最长合法括号
思路:用栈。一开始想的太简单,但没那么简单。难点在于如何寻找合法串的开始。例如(() 这种,应该怎样记录呢?
但事实上应该换一个角度:
stack里面装的一直是“还没配好对的那些可怜的括号的index”是'(‘的时候push
是’)’的时候,说明可能配对了;看stack top是不是左括号,不是的话,push当前的’)’(算是一种对之前push进去的所有东西的清除)
是的话,pop那个配对的左括号,然后update res:i和top的(最后一个配不成对的)index相减,就是i属于的这一段的当前最长。如果一pop就整个栈空了,说明前面全配好对了,那res就是最大=i+1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public int longestValidParentheses (String s) Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); int max = 0 , curr = 0 ; char [] arr = s.toCharArray(); for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.length; ++i){ if (arr[i] == ')' && !stack.empty() && arr[stack.peek()] == '(' ){ stack.pop(); if (stack.empty()){ max = i + 1 ; }else { max = Math.max(max, i - stack.peek()); } }else { stack.push(i); } } return max; }
Flatten Nested List Iterator
给一个被嵌套的整数list [[1,1],2,[1,1]]。 要实现这个嵌套列表的hasNext和Next方法。
一开始我用的递归,最后边界条件怎么都过不去。差点气死。
其实应该是在hasNext里面就进行好转换的。哎。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 Stack<NestedInteger> stack = new Stack<>(); public NestedIterator (List<NestedInteger> nestedList) for (int i = nestedList.size() - 1 ; i >= 0 ; --i){ stack.push(nestedList.get(i)); } } @Override public Integer next () return stack.pop().getInteger(); } @Override public boolean hasNext () if (stack.empty()) return false ; while (!stack.empty() && !stack.peek().isInteger()){ List<NestedInteger> list = stack.pop().getList(); for (int i = list.size() - 1 ; i >= 0 ; --i){ stack.push(list.get(i)); } } return !stack.empty(); }
Exclusive Time of Functions
题意:给定一组函数调用日志,格式为"function_id:start_or_end:timestamp",函数可以递归。求每个函数调用的总时长。
约定:(1)输入日志将按时间戳记排序,而不是日志ID;(2)输出应按函数id排序;(3)两个函数不会同时开始或结束;(4)函数可以递归调用,并且将最终都会结束;(5)1<= n<= 100。
这道题一开始我想多了,用了两个栈。其实只用一个就好。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public int [] exclusiveTime(int n, List<String> logs) { Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); int [] result = new int [n]; String start = "start" ; int prevTime = 0 ; for (String log : logs){ String[] status = log.split(":" ); if (!stack.isEmpty())result[stack.peek()] += (Integer.valueOf(status[2 ]) - prevTime); prevTime = Integer.valueOf(status[2 ]); if (status[1 ].equals(start)){ stack.push(Integer.valueOf(status[0 ])); }else { result[stack.pop()]++; prevTime++; } } return result; }
给一个字符串"(*))"。 星号代表左括号或右括号或空。求这个括号串是否合法。
计算问题
Evaluate Reverse Polish Notation
计算Reverse Polish Notation 形式的数字。即:
1 2 ["2", "1", "+", "3", "*"] -> ((2 + 1) * 3) -> 9 ["4", "13", "5", "/", "+"] -> (4 + (13 / 5)) -> 6
思路:栈!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 private boolean isNum (String s) if (s.equals("+" ) || s.equals("-" ) || s.equals("*" ) || s.equals("/" )) return false ; return true ; } public int evalRPN (String[] tokens) if (tokens.length == 0 ) return 0 ; Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>(); for (String token : tokens){ if (isNum(token)){stack.push(token); continue ;} int val2 = Integer.valueOf(stack.pop()); int val1 = Integer.valueOf(stack.pop()); int currResult = 0 ; if (token.equals("+" )){currResult = val1 + val2;} else if (token.equals("-" )){currResult = val1 - val2;} else if (token.equals("*" )){currResult = val1 * val2;} else currResult = val1 / val2; stack.push(String.valueOf(currResult)); } return Integer.valueOf(stack.pop()); }
Basic Calculator II
求一个计算式的值。其中计算式含加减乘除,但不含括号。
方法1,栈
一开始没想明白。其实思路很简单。
因为乘法和除法不仅要知道下一个数,也要知道上一个数。所以我们用一个栈把上次的数存起来,遇到加减法就直接将数字压入栈中,遇到乘除法就把栈顶拿出来乘或除一下新数,再压回去。最后我们把栈里所有数加起来就行了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 private int [] getNum(String s, int i){ int num = 0 ; while (i < s.length()){ if (Character.isDigit(s.charAt(i))){ num = num * 10 + (int )(s.charAt(i) - '0' ); ++i; }else if (s.charAt(i) == ' ' ){ ++i; }else { break ; } } return new int []{num, i}; } public int calculate (String s) if (s.length() == 0 ) return 0 ; int i = 0 ; Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); char sig = '+' ; while (i < s.length()){ if (!Character.isDigit(s.charAt(i)) && s.charAt(i) != ' ' ){ sig = s.charAt(i); ++i; } int [] temp = getNum(s, i); int num = temp[0 ]; i = temp[1 ]; if (sig == '+' ) stack.push(num); else if (sig == '-' ) stack.push(-num); else if (sig == '*' ){ if (stack.empty()) stack.push(num); else stack.push(stack.pop() * num); } else if (sig == '/' ){ if (stack.empty()) stack.push(num); else stack.push(stack.pop() / num); } } int result = 0 ; while (!stack.isEmpty()){ result += stack.pop(); } return result; }
方法2
栈只是在乘除的时候用到,而且仅仅用到了上一个数字。因此我们可以去掉栈,只需要保留上一个数字。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 private int [] getNum(String s, int i){ int num = 0 ; while (i < s.length()){ if (Character.isDigit(s.charAt(i))){ num = num * 10 + (int )(s.charAt(i) - '0' ); ++i; }else if (s.charAt(i) == ' ' ){ ++i; }else { break ; } } return new int []{num, i}; } public int calculate (String s) if (s.length() == 0 ) return 0 ; int i = 0 ; char sig = '+' ; int result = 0 ; int [] temp = getNum(s, i); int lastNum = temp[0 ]; i = temp[1 ]; while (i < s.length()){ if (!Character.isDigit(s.charAt(i)) && s.charAt(i) != ' ' ){ sig = s.charAt(i); ++i; } temp = getNum(s, i); int num = temp[0 ]; i = temp[1 ]; if (sig == '+' ) { result += lastNum; lastNum = num; } else if (sig == '-' ) { result += lastNum; lastNum = -num; } else if (sig == '*' ){ lastNum = lastNum * num; } else if (sig == '/' ){ lastNum = lastNum / num; } } return result + lastNum; }
Basic Calculator
这是上一题的升级版。计算带括号的加减法。
我的思路是将括号内部的运算看做一个整体。但事实上之后看题才知道没有乘除。。。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 public int [] calculateBase(String s, int i) { if (i >= s.length()) return new int []{i, 0 }; int result = 0 ; int LastNum = 0 ; while (i < s.length()){ if (s.charAt(i) == ')' ){ ++i; break ; } char sig = '+' ; if (!Character.isDigit(s.charAt(i)) && s.charAt(i) != ' ' && s.charAt(i) != '(' && s.charAt(i) != ')' ){ sig = s.charAt(i); ++i; } int num = 0 ; if (s.charAt(i) == '(' ){ int [] temp = calculateBase(s, i + 1 ); i = temp[0 ]; num = temp[1 ]; }else { num = 0 ; while (i < s.length()){ if (Character.isDigit(s.charAt(i))){ num = num * 10 + (int )(s.charAt(i) - '0' ); ++i; }else if (s.charAt(i) == ' ' ){ ++i; }else { break ; } } } if (sig == '+' ){ result += LastNum; LastNum = num; }else if (sig == '-' ){ result += LastNum; LastNum = -num; } return new int []{i, result + LastNum}; } public int calculate (String s) return calculateBase(s, 0 )[1 ]; }
大神代码
自己写的依然很啰嗦。下面瞻仰一下大神的代码。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 public int calculate (String s) if (s==null || s.length()==0 ) return 0 ; Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>(); int result = 0 ; int num = 0 ; int multiplier = 1 ; for (int i=0 ; i<s.length(); i++) { char c = s.charAt(i); if (c>='0' && c<='9' ) { int digit = c-'0' ; num = num*10 + digit; } else if (c=='+' ) { result += num*multiplier; num = 0 ; multiplier = 1 ; } else if (c=='-' ) { result += num*multiplier ; num = 0 ; multiplier =-1 ; } else if (c=='(' ) { stack.push(result); stack.push(multiplier); result = 0 ; multiplier = 1 ; } else if (c==')' ) { result += num*multiplier; result *= stack.pop(); result += stack.pop(); num = 0 ; } } result += num*multiplier; return result; }
Basic Calculator III
带括号的加减乘除。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 public int [] calculateBase(String s, int i) { if (i >= s.length()) return new int []{i, 0 }; int result = 0 ; int LastNum = 0 ; while (i < s.length()){ while (i < s.length() && s.charAt(i) == ' ' ){ ++i; } if (s.charAt(i) == ')' ){ ++i; break ; } char sig = '+' ; if (!Character.isDigit(s.charAt(i)) && s.charAt(i) != ' ' && s.charAt(i) != '(' && s.charAt(i) != ')' ){ sig = s.charAt(i); ++i; } while (i < s.length() && s.charAt(i) == ' ' ){ ++i; } int num = 0 ; if (s.charAt(i) == '(' ){ int [] temp = calculateBase(s, i + 1 ); i = temp[0 ]; num = temp[1 ]; }else { num = 0 ; while (i < s.length()){ if (Character.isDigit(s.charAt(i))){ num = num * 10 + (int )(s.charAt(i) - '0' ); ++i; }else if (s.charAt(i) == ' ' ){ ++i; }else { break ; } } } if (sig == '+' ){ result += LastNum; LastNum = num; }else if (sig == '-' ){ result += LastNum; LastNum = -num; }else if (sig == '*' ){ LastNum = num * LastNum; }else if (sig == '/' ){ LastNum = LastNum / num; } } while (i < s.length() && s.charAt(i) == ' ' ){ ++i; } return new int []{i, result + LastNum}; } public int calculate (String s) return calculateBase(s, 0 )[1 ]; }
其它问题
Simplify Path
简化路径。path = "/a/./b/../../c/", => "/c"
此题我觉得关键之处在于,知道路径是由/ 符号分割的。因此可以用/ 号分割后计算
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 /../代表上一层路径 /./代表本层路径 private String helper (String path) Deque<String> stack = new LinkedList<>(); String[] segments = path.split("/" ); for (String seg : segments){ if (seg.length()== 0 ) continue ; if (seg.equals(".." )){ if (!stack.isEmpty()) stack.pop(); }else if (seg.equals("." )){continue ;} else { stack.push(seg); } } StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); while (!stack.isEmpty()){ sb.append("/" ); sb.append(stack.pollLast()); } return sb.length() == 0 ? "/" : sb.toString(); } public String simplifyPath (String path) return helper(path); }
Longest Absolute File Path
给一个路径"dir\n\tsubdir1\n\tsubdir2\n\t\tfile.ext"。 其中\n\t file 代表第一层路径下的文件file ,\n\t\t 代表第二层路径下的文件。比如上面给的这个路径表示
1 2 3 4 dir subdir1 subdir2 file.ext
求一个路径str下,路径的字符个数最多的那个文件的路径字符个数
思路:用两个栈。一个栈维护当前的深度(即第几层文件),另一个栈维护当前文件的路径字符个数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 private int count_t (String s) int count = 0 ; while (count < s.length() && s.charAt(count) == '\t' ){ ++count; } return count; } private boolean isFile (String s) int count = 0 ; for (char c : s.toCharArray()){ if (c == '.' ) ++count; } return count > 0 ; } public int lengthLongestPath (String input) String[] sub = input.split("\n" ); if (sub.length == 0 ) return 0 ; Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); Stack<Integer> deep = new Stack<>(); stack.push(sub[0 ].length() + 1 ); deep.push(0 ); int max = isFile(sub[0 ]) ? stack.peek() - 1 : 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < sub.length; ++i){ int deepCurr = count_t(sub[i]); while (!deep.empty() && deepCurr <= deep.peek()){ stack.pop(); deep.pop(); } if (stack.empty()){ stack.push(sub[i].length() - deepCurr + 1 ); }else stack.push(stack.peek() + sub[i].length() - deepCurr + 1 ); deep.push(deepCurr); if (isFile(sub[i])){ max = Math.max(stack.peek() - 1 , max); } } return max; }
Min Stack
实现一个能实时输出最小值的栈。
思路一:栈 + 优先队列
/** initialize your data structure here. */
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 class Node implements Comparable <Node > long val; boolean deleted; Node(int val) { this .val = val; deleted = false ; } @Override public int compareTo (Node o) if (this .val - o.val >= 0 ){ return 1 ; }else { return -1 ; } } } LinkedList<Node> links; PriorityQueue<Node> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(); public MinStack () links = new LinkedList<>(); priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(); } public void push (int x) Node xNode = new Node(x); links.addFirst(xNode); priorityQueue.add(xNode); } public void pop () Node removed = links.removeFirst(); removed.deleted = true ; } public int top () return (int )links.get(0 ).val; } public int getMin () while (priorityQueue.peek().deleted){ priorityQueue.poll(); } return (int )priorityQueue.peek().val; }
思路2,骚操作
对于当前已经入栈的元素来说,维护当前入栈元素的最小值。相当鸡贼
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE; Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<>(); public void push (int x) if (x<=min){ stack.push(min); min=x; } stack.push(x); } public void pop () if (stack.pop()== min) min=stack.pop(); } public int top () return stack.peek(); } public int getMin () return min; }
Hash
\(O(1)\) 插入
\(O(1)\) 查找
\(O(1)\) 删除
问题: Hash Table / Hash Map / Hash Set 的区别是什么? Hash Table - 线程安全 Hash Map - 线程不安全
String的Hash实现原理,复杂度\(O(L)\)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 int hashfunc (String key) int sum = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < key.length(); ++i){ sum = sum * 31 + (int )(key.charAt(i)); sum = sum % HASH_TABLE_SIZE; } }
相当于\(ab =mod (a \times 31^2 + b \times 31)\)
解决Hash冲突的两种办法:
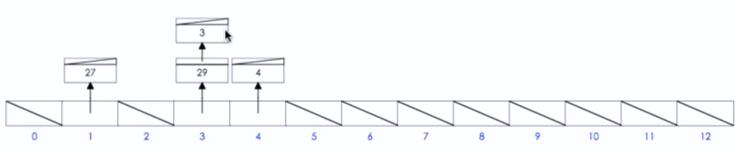
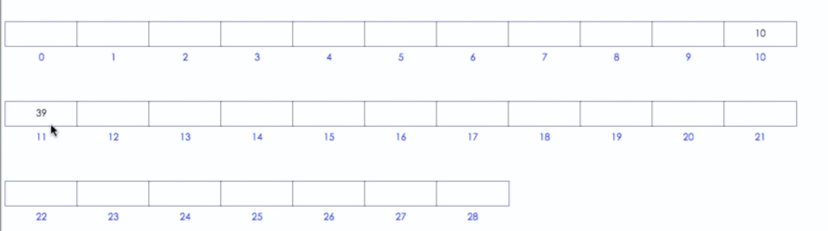
Open Hashing : 开散列/拉链法。每个地方都是一个链表
Close Hashing : 线性探测法。 10和39的idx一样。10先插入,因此39插入时就依次放入下一个坑
ReHahsing
解决放不下的问题? —— 不够了就乘2
这是一道题,回头看看
例题1, LRU Cache
双链表 + Hash
Word Pattern
给两个字符串,判断这两个字符串是否能匹配。匹配的样例如下:
pattern = "abba", str = "dog cat cat dog" should return true.
pattern = "abba", str = "dog cat cat fish" should return false.
pattern = "aaaa", str = "dog cat cat dog" should return false.
pattern = "abba", str = "dog dog dog dog" should return false.
思路:双hash表进行一一映射。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public boolean wordPattern (String pattern, String str) String[] str_arr = str.split(" " ); if (str_arr.length != pattern.length())return false ; HashMap<Character, String> map = new HashMap<>(); HashMap<String, Character> str2charMap = new HashMap<>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < pattern.length(); ++i){ if (map.containsKey(pattern.charAt(i))){ if (!map.get(pattern.charAt(i)).equals(str_arr[i])) return false ; }else { if (str2charMap.containsKey(str_arr[i])) return false ; map.put(pattern.charAt(i), str_arr[i]); str2charMap.put(str_arr[i], pattern.charAt(i)); } } return true ; }
Insert Delete GetRandom O(1)
设计一个数据结构,支持插入、删除和随机取的复杂度都是\(O(1)\)
注意一些技巧,特别是remove时的技巧。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 HashMap<Integer, Integer> set; ArrayList<Integer> nums; java.util.Random rand = new java.util.Random(); public RandomizedSet () set = new HashMap<>(); nums = new ArrayList<>(); } public boolean insert (int val) if (set.containsKey(val)) return false ; set.put(val,nums.size()); nums.add(val); return true ; } public boolean remove (int val) if (set.containsKey(val)){ int idx = set.get(val); int lastVal = nums.get(nums.size() - 1 ); set.replace(lastVal, idx); nums.set(idx,lastVal); set.remove(val); nums.remove(nums.size() - 1 ); return true ; }else return false ; } public int getRandom () return nums.get(rand.nextInt(nums.size())); }
Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) - Duplicates allowed
如果允许重复元素出现,那么怎么实现?
那就把idx变成idx列表!
(为什么不能直接计数呢?因为如果只计数的话,随机输出时,元素比例就不符合原来的比例了)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 HashMap<Integer, ArrayList<Integer>> set; ArrayList<Integer> nums; Random rand = new Random(); public RandomizedCollection () set = new HashMap<>(); nums = new ArrayList<>(); } public boolean insert (int val) if (set.containsKey(val)){ set.get(val).add(nums.size()); nums.add(val); return false ; }else { ArrayList idxs = new ArrayList<>(); idxs.add(nums.size()); set.put(val,idxs); nums.add(val); return true ; } } public boolean remove (int val) if (set.containsKey(val)){ ArrayList<Integer> idxs = set.get(val); if (idxs.get(0 ) < nums.size() - 1 ) { nums.set(idxs.get(0 ), nums.get(nums.size() - 1 )); ArrayList<Integer> lastIdxs = set.get(nums.get(idxs.get(0 ))); int deleted = 0 ; while (deleted < lastIdxs.size()) { if (lastIdxs.get(deleted) == nums.size() - 1 ) { lastIdxs.remove(deleted); } deleted += 1 ; } lastIdxs.add(idxs.get(0 )); } nums.remove(nums.size() - 1 ); if (idxs.size() == 1 ){set.remove(val);} else {idxs.remove(0 );} return true ; }else { return false ; } } public int getRandom () if (nums.size() == 0 ) return -1 ; return nums.get(rand.nextInt(nums.size())); }
Sort Characters By Frequency
题意:给一个字符串"tree",按照字母频率输出“eetr”或"eert"
思路:直接用hashMap统计每个字符的次数,然后按照次数排序并输出。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution public String frequencySort (String s) HashMap<Character,Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); for ( char c : s.toCharArray() ){ if ( map.containsKey(c) ){ map.replace(c,map.get(c)+1 ); }else { map.put(c,1 ); } } List<Map.Entry<Character,Integer>> list = new LinkedList<Map.Entry<Character,Integer>>(map.entrySet()); Collections.sort( list, new Comparator<Map.Entry<Character,Integer>>() { public int compare (Map.Entry<Character,Integer> o1, Map.Entry<Character,Integer> o2) return (o2.getValue()).compareTo( o1.getValue() ); } }); int times; StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(s.length()); for (Map.Entry<Character,Integer> entry : list) { times = entry.getValue(); while (times>0 ){ result.append(entry.getKey()); --times; } } return result.toString(); } }
这道题还有另一种精妙的O(n)思路,只是有点浪费空间:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public String frequencySort (String s) Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); for (char c : s.toCharArray()) { if (map.containsKey(c)) { map.put(c, map.get(c) + 1 ); } else { map.put(c, 1 ); } } List<Character> [] bucket = new List[s.length() + 1 ]; for (char key : map.keySet()) { int frequency = map.get(key); if (bucket[frequency] == null ) { bucket[frequency] = new ArrayList<>(); } bucket[frequency].add(key); } StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); for (int pos = bucket.length - 1 ; pos >=0 ; pos--) { if (bucket[pos] != null ) { for (char num : bucket[pos]) { for (int i = 0 ; i < map.get(num); i++) { sb.append(num); } } } } return sb.toString(); }
堆
下节课讲
 缺点:删除时,需要将删掉的这个元素直接设置为deleted
缺点:删除时,需要将删掉的这个元素直接设置为deleted 