在学系统设计的时候设计到了缓存过期算法。在此详细研究一下介个。
本文主要参考自详解三种缓存过期策略LFU,FIFO,LRU(附带实现代码)
缓存机制:先分配一定的缓存空间。使用数据的时候先查询缓存空间中是否有该数据的缓存。如果有的话直接拿出来。如果没有的话去其它地方查询,然后同时将查询到的结果放入缓存空间,方便下次调用。伪代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 def getUser (user_id ): user = cache.get(user_id) if user : return user user = database.get(user_id) cache.set (key, user) return user def setUser (user ): cache.delete(user.user_id) database.set (user)
缓存机制就像上面所说的那样。cache 一般是有有效期的,也就是如果缓存中这个数据过期了,那就从缓存中清理出去。而cache 的实现过程和淘汰机制不同,会导致不同的性能表现。常见的就是IFIO,LRU,LFU缓存过期策略。
FIFO(First In First Out) : 先进先出。淘汰掉很久以前进来的数据,而新数据等到之后再淘汰。也就是一个队列。
LRU (Least recently used) : 最近最少使用。淘汰最近不适用的数据
LFU (Least frequently used) : 最近使用次数最少。淘汰掉使用次数最少的页面。
FIFO
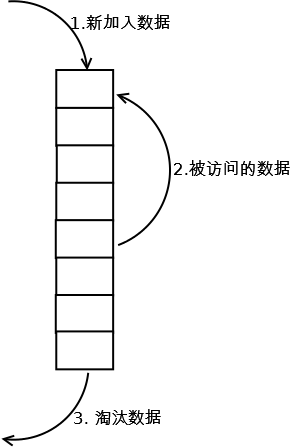
按照“先进先出(First In,First Out)”的原理淘汰数据,正好符合队列的特性,数据结构上使用队列Queue来实现。
如下图:
新访问的数据插入FIFO队列尾部,数据在FIFO队列中顺序移动;
淘汰FIFO队列头部的数据;
LRU
(Least recently used,最近最少使用)算法根据数据的历史访问记录来进行淘汰数据,其核心思想是“如果数据最近被访问过,那么将来被访问的几率也更高”。
最常见的实现是使用一个链表保存缓存数据,详细算法实现如下:
新数据插入到链表头部;
每当缓存命中(即缓存数据被访问),则将数据移到链表头部;
当链表满的时候,将链表尾部的数据丢弃。
LeetCode题:146. LRU Cache
要用O(1)的时间复杂度完成LRU算法。
我的思路:双链表 + HashMap<key, Node>
代码贼长
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 class LinkList class Node int key; int val; Node next; Node prev; Node(int key,int val){ this .val = val; this .key = key; next = null ; prev = null ; } } Node dummyHead; Node dummyTail; int size; int capacity; HashMap<Integer, Node> keyNodeHash; LinkList(int capacity){ dummyHead = new Node(0 ,0 ); dummyTail = new Node(0 ,0 ); dummyHead.next = dummyTail; dummyTail.prev = dummyHead; this .capacity = capacity; size = 0 ; keyNodeHash = new HashMap<>(); } public void add (int key, int val) if (keyNodeHash.containsKey(key)){ Node e = keyNodeHash.get(key); e.val = val; setFirst(e); return ; } if (size >= capacity){ keyNodeHash.remove(deleteTail().key); } keyNodeHash.put(key, addFirst(key, val)); } public int getValue (int key) if (keyNodeHash.containsKey(key)){ Node setFirstNode = keyNodeHash.get(key); setFirst(setFirstNode); return keyNodeHash.get(key).val; } return -1 ; } private Node addFirst (Node curr) curr.next = dummyHead.next; dummyHead.next.prev = curr; dummyHead.next = curr; curr.prev = dummyHead; ++size; return curr; } private Node addFirst (int key, int val) Node curr = new Node(key, val); return addFirst(curr); } private void setFirst (Node e) queue.delete(e); queue.addFirst(e); } private void delete (Node e) Node prev = e.prev; Node next = e.next; prev.next = next; next.prev = prev; e.prev = null ; e.next = null ; --size; } private Node deleteTail () Node deleted = dummyTail.prev; delete(deleted); return deleted; } } LinkList queue ; public LRUCache (int capacity) queue = new LinkList(capacity); } public int get (int key) return queue.getValue(key); } public void put (int key, int value) queue.add(key, value); }
LFU
(Least Frequently Used)算法根据数据的历史访问频率来淘汰数据,其核心思想是“如果数据过去被访问多次,那么将来被访问的频率也更高”。
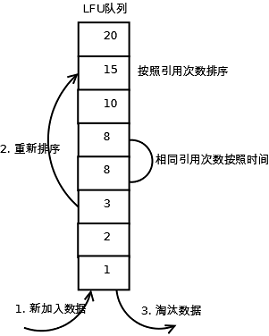
LFU的每个数据块都有一个引用计数,所有数据块按照引用计数排序,具有相同引用计数的数据块则按照时间排序。
具体实现如下:
新加入数据插入到队列尾部(因为引用计数为1);
队列中的数据被访问后,引用计数增加,队列重新排序;
当需要淘汰数据时,将已经排序的列表最后的数据块删除。
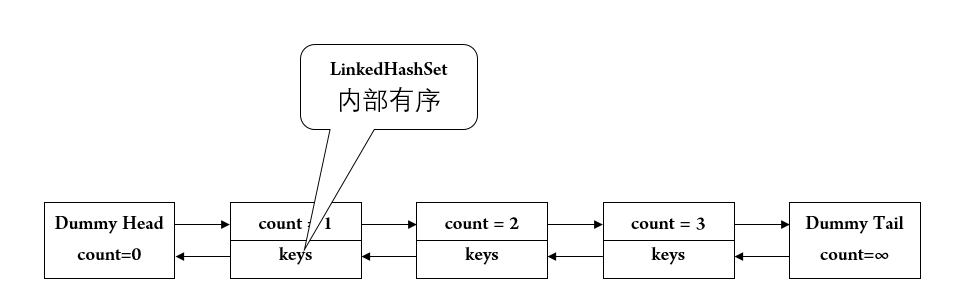
实现时,我们只需要考虑keys的增删,然后再外部保持一个key,value的对应关系即可。数据结构的设计如下所示:
首先这是一个双链表。链表的每个节点为:
1 2 3 4 class Node int count; LinkedHashSet<Integer> keys; }
其中,keys是一个LinkedHashSet,它可以按照数据的插入顺序输出,每次输出都是先输出老数据,最后输出新数据。
我们以leetcode给的样例说明:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 LFUCache cache = new LFUCache( 2 /* capacity */ ); cache.put(1, 1); cache.put(2, 2); cache.get(1); // returns 1 cache.put(3, 3); // evicts key 2 cache.get(2); // returns -1 (not found) cache.get(3); // returns 3. cache.put(4, 4); // evicts key 1. cache.get(1); // returns -1 (not found) cache.get(3); // returns 3 cache.get(4); // returns 4
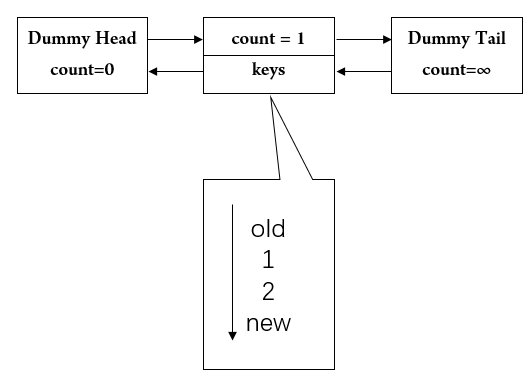
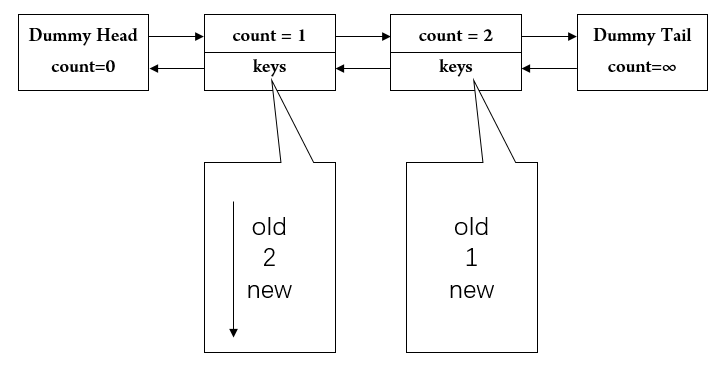
一开始插入cache.put(1, 1); cache.put(2, 2); ,变成这样
然后我们执行cache.get(1); // returns 1,那么变成了:
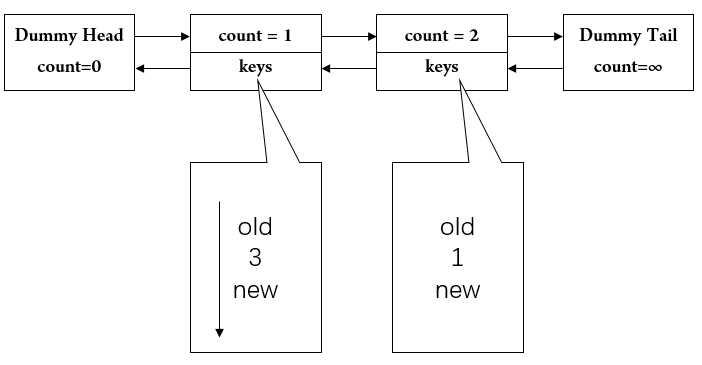
然后我们执行cache.put(3, 3); // evicts key 2 。此时数据个数大于容量2了,就要先把最老的删除,也就是2,然后插入新数据。变成了:
之后的操作不再画图阐述。
那么总的伪代码为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 List<Node> lists; HashMap <key, value> kv; public int get (int key) if not exsit <key,value> in kv, return -1 else move key to next Node return key.value } public void put (int key, int value) if exsit <key,OldValue> in kv : remove key from key.node put <key,value> to kv add <key> to count=1 node }
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 class Node Node next; Node prev; LinkedHashSet<Integer> keys; int count; Node(int count){ this .count = count; keys = new LinkedHashSet<>(); next = null ; prev = null ; } } private Node dummyHead; private Node dummyTail; private HashMap<Integer, Integer> keyValueMap; private HashMap<Integer,Node> keyNodeMap; int capacity; public LFUCache (int capacity) this .capacity = capacity; keyValueMap = new HashMap<>(); keyNodeMap = new HashMap<>(); dummyHead = new Node(0 ); dummyTail = new Node(Integer.MAX_VALUE); dummyHead.next = dummyTail; dummyTail.prev = dummyHead; } public int get (int key) if (keyValueMap.containsKey(key)){ increaseCount(key); return keyValueMap.get(key); } return -1 ; } public void put (int key, int value) if (capacity == 0 ) return ; if (keyValueMap.containsKey(key)){ keyValueMap.put(key,value); }else { if (keyValueMap.size() >= capacity){ removeOld(); } keyValueMap.put(key,value); addTohead(key); } increaseCount(key); } private void addTohead (int key) dummyHead.keys.add(key); keyNodeMap.put(key, dummyHead); } private void increaseCount (int key) Node node = keyNodeMap.get(key); node.keys.remove(key); keyNodeMap.remove(key); if (node.next == dummyTail){ addNext(node); } node.next.keys.add(key); keyNodeMap.put(key, node.next); } private void addNext (Node node) Node newNext = new Node(node.count + 1 ); newNext.next = node.next; newNext.prev = node; node.next.prev = newNext; node.next = newNext; } private void removeOld () if (keyValueMap.size() == 0 ) return ; Node curr = dummyHead; while (curr.keys.isEmpty()){ curr = curr.next; } int LFUKey = 0 ; for (int n : curr.keys){ LFUKey = n; break ; } curr.keys.remove(LFUKey); keyNodeMap.remove(LFUKey); keyValueMap.remove(LFUKey); }
注:本来想着用优先队列实现。但是不知道为什么有样例不能通过。气死了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 public class LFUCache private static int time = 0 ; class Node implements Comparable <Node > int counter; int key; int value; int timeStamp; Node(int key, int value){ this .key = key; this .value = value; this .timeStamp = time++; this .counter = 1 ; } public void reset (int value) this .counter = 1 ; this .value = value; this .timeStamp = time++; } public String toString () return " key=" + key + ",value=" + value + ",counter=" + counter; } @Override public int compareTo (Node o) if (this .counter == o.counter) return this .timeStamp - o.timeStamp; return this .counter - o.counter; } } class PivotQueue PivotQueue(int capcity){ this .capcity = capcity; } private int size = 0 ; private int capcity; private ArrayList<Node> arr = new ArrayList<>(); public HashMap<Integer, Node> keyIdxMap = new HashMap<>(); public int getSize () return size; } private int getLeft (int i) return (i << 1 ) + 1 ; } private int getRight (int i) return (i << 1 ) + 2 ; } private int getParent (int i) return (i - 1 ) >> 1 ; } public int getValue (int key) if (capcity==0 ) return -1 ; if (!keyIdxMap.containsKey(key)) return -1 ; else { Node curr = keyIdxMap.get(key); return get(curr); } } public void add (int key, int value) if (capcity==0 )return ; System.out.println(time + " adding " +key+"\t" +value); if (keyIdxMap.containsKey(key)){ reset(arr.indexOf(keyIdxMap.get(key)), value); return ; } while (size >= capcity){ poll(); } Node curr = new Node(key, value); arr.add(curr); keyIdxMap.put(curr.key, curr); shiftUp(arr.size() - 1 ); shiftDown(arr.indexOf(curr)); ++size; } private int poll () int result = arr.get(0 ).value; keyIdxMap.remove(arr.get(0 ).key); swap(0 , arr.size() - 1 ); arr.remove(arr.size() - 1 ); --size; shiftDown(0 ); return result; } private int get (Node curr) int result = curr.value; ++curr.counter; curr.timeStamp = time++; shiftDown(arr.indexOf(curr)); return result; } private void reset (int i, int value) arr.get(i).reset(value); shiftUp(i); shiftDown(i); } private void swap (int i, int j) Node a = arr.get(i); int aCounter = a.counter, aKey = a.key, aValue = a.value, aTimeStamp = a.timeStamp; Node b = arr.get(j); a.counter = b.counter; a.key = b.key; a.value = b.value; a.timeStamp = b.timeStamp; b.counter = aCounter; b.key = aKey; b.value = aValue; b.timeStamp = aTimeStamp; keyIdxMap.replace(a.key, a); keyIdxMap.replace(b.key, b); } private void shiftUp (int i) if (i == 0 || arr.get(i).compareTo(arr.get(getParent(i))) > 0 ){ return ; } swap(i, getParent(i)); shiftUp(getParent(i)); } private void shiftDown (int i) if (i >= arr.size()) return ; int left = getLeft(i), right = getRight(i); if (left >= arr.size() && right >= arr.size()) return ; int smallest = i; if (left < arr.size() && arr.get(smallest).compareTo(arr.get(left)) > 0 ){ smallest = left; } if (right < arr.size() && arr.get(smallest).compareTo(arr.get(right)) > 0 ){ smallest = right; } if (smallest == i) return ; swap(smallest, i); shiftDown(smallest); } } PivotQueue pivotQueue; public LFUCache (int capacity) pivotQueue = new PivotQueue(capacity); } public int get (int key) int result = pivotQueue.getValue(key); System.out.println(time + " getting " +key + " result = " + result); return result; } public void put (int key, int value) pivotQueue.add(key, value); } public static void main (String[] arg) LFUCache obj = new LFUCache(2 ); obj.put(1 ,1 ); obj.put(2 ,2 ); obj.get(1 ); obj.put(3 ,3 ); obj.get(2 ); obj.get(3 ); obj.put(4 ,4 ); obj.get(1 ); System.out.println(obj.get(3 ));; System.out.println(obj.get(4 ));; } }